Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) has transformed how businesses and households make calls. Instead of relying on traditional phone lines, VoIP allows conversations to travel over the internet. But how exactly does a VoIP phone work? Let’s break it down step by step.
What Is VoIP?
VoIP, or Voice over Internet Protocol, is a technology that converts voice signals into digital data and transmits them over the internet. This means you don’t need a traditional landline — just an internet connection and a VoIP-compatible device.
The Process: How Calls Travel Through VoIP
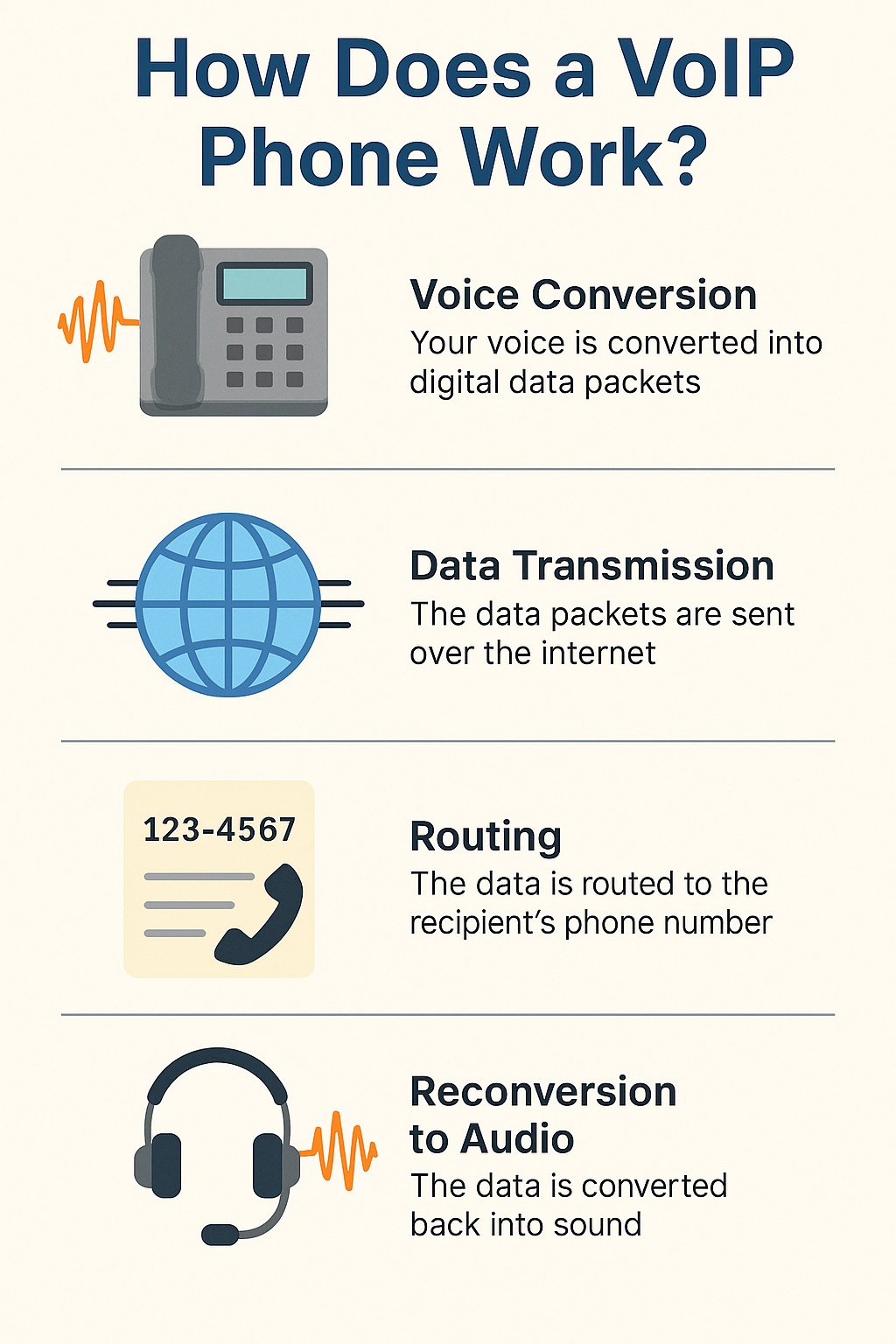
- Voice Conversion
- When you speak into a VoIP phone, your voice (analog sound waves) is converted into digital packets of data.
- Data Transmission
- These packets are sent over the internet using your broadband connection, similar to how emails or videos are transmitted.
- Routing
- The data is routed to the recipient’s phone number or VoIP address. If you’re calling a traditional landline, a VoIP gateway converts the packets back into a standard phone signal.
- Reconversion to Audio
- On the other end, the recipient’s device converts the digital packets back into voice that they can hear in real time.
Devices You Can Use for VoIP Calls
- VoIP desk phones: Look like traditional phones but connect via Ethernet or Wi-Fi.
- Softphones: Software apps (like Zoom, Skype, or Microsoft Teams) that let you call using a computer or smartphone.
- Adapters: Let you connect a traditional landline handset to a VoIP service via your internet router.
Benefits of VoIP Phones
- Cost Savings: Cheaper long-distance and international calls.
- Flexibility: Use the same number anywhere with an internet connection.
- Features: VoIP services often include voicemail-to-email, call forwarding, video calls, and conferencing.
- Scalability: Easy to add or remove lines without new wiring.
Common Requirements for VoIP to Work Smoothly
- Reliable broadband internet (wired is better than Wi-Fi).
- Good router and network setup to avoid delays or dropped calls.
- Power backup — since VoIP depends on electricity and internet, an outage means no calls unless you have a battery backup or mobile failover.
Final Thoughts
A VoIP phone works by turning your voice into data, transmitting it online, and reconverting it into sound at the other end. With lower costs, rich features, and flexibility, VoIP has become the standard for both businesses and home communication.

Leave a Reply